Standards and Interoperability
Arches was designed with the consultation and incorporation of internationally adopted standards for information technology. Standards are agreed-upon requirements, guidelines, and specifications to ensure consensus, quality, interoperability, and security of technologies and data resources.
Interoperability, or the ability for two distinct systems to exchange information, is critical for long-term data management and stewardship, to ensure the discovery, evaluation, and reuse of these data. Because of this, Arches utilizes standards that support FAIR (Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reuse) data principles.
Examples of standards supported by Arches
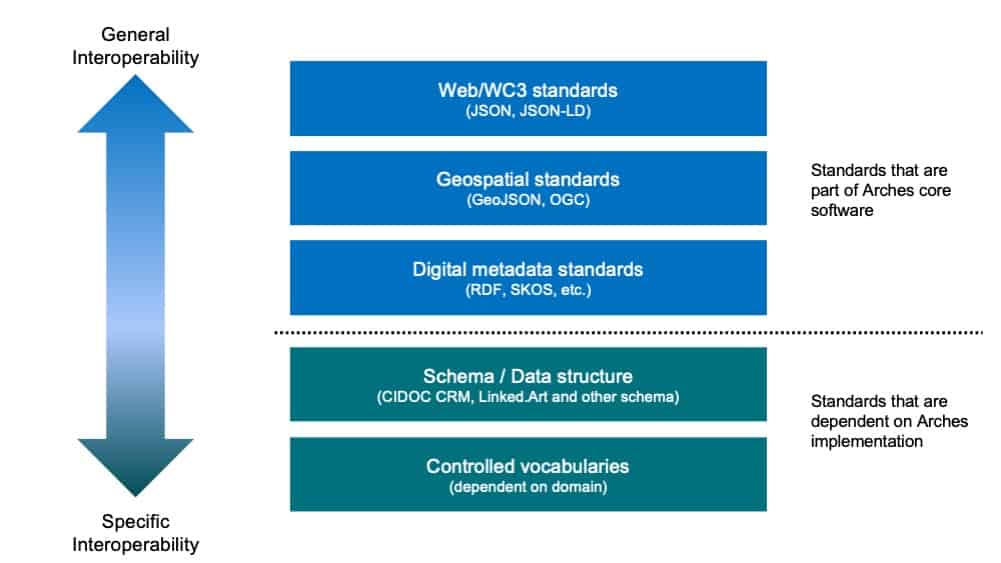
The following diagram shows the different kinds of standards supported by Arches, whether they are part of the core Arches code or dependent on the requirements of an Arches implementation, and where they fall on the spectrum between achieving general interoperability and specific interoperability. In this case, general interoperability is domain-agnostic and relates primarily to data and web standards, while specific interoperability applies to particular use cases and domains. For example, JSON is a standard that is broadly accepted and utilized by technical communities, while the CIDOC Conceptual Reference Model (CRM) is an ontology that defines cultural heritage data and data relationships.
Below are examples of standards that Arches supports.
Web/WC3 standards
- JSON: An open-standard file format that stores and transmits data objects and is used in web applications and servers.
- JSON-LD: A method for encoding linked data as JSON.
Geospatial standards
- GeoJSON: A JSON encoding format for geographic data structures.
- Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) Standards: Standards that enable interoperability between geospatial software and services.
Digital metadata standards
- Resource Description Framework (RDF): Standard data model for data exchange on the web.
- Simple Knowledge Organization System (SKOS): Standardization of thesauri, classification schemas, taxonomies, and other controlled vocabularies.
Schema / data structure (standards implemented during the modeling process*)
- CIDOC Conceptual Reference Model (CRM): Ontology for cultural heritage information and the relationships between related concepts (adopted as ISO 21127:2023).
- Linked.Art: A shared conceptual model to describe Art with Linked Open Data.
Controlled vocabularies (standards implemented during the modeling process*)
- Getty AAT: The Getty Art and Architecture Thesaurus is a multilingual, structured vocabulary for describing and indexing the visual arts and architecture.
Non-proprietary or open file formats
In addition to the above standards, Arches uses a variety of non-proprietary or open file formats for tabular data (e.g. .csv, .txt), images (e.g. .jpg, .png), web data (e.g. .json, .xml, .html), geospatial data (e.g. .tiff, .shp), text files (e.g. .txt, .pdf, .html), and more. The use of non-proprietary or open file formats helps to ensure that data is not locked in closed proprietary file formats that require specific software to access.
*For information on implementing standards during the modeling process, please refer to the Modeling Documentation page.
Last updated: August 2024